Understanding Coal-Fired Boilers: How They Work, Benefits, and Environmental Impact
Coal-fired boilers happen to be a backbone of industrial and power generation sectors for over a century. Despite growing interest in renewable energy, coal-fired systems always play an important role in many countries due to their ability to produce a lot of energy at relatively low priced. This article explores the function, benefits, and drawbacks of coal fired boiler, together with modern advancements directed at reducing their environmental impact. What Is a Coal-Fired Boiler? A coal-fired boiler is a type of commercial boiler which uses coal as its primary fuel to generate steam. This steam might be used to drive turbines for electricity generation as well as to provide heat for various industrial processes. 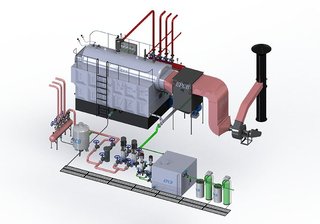 Main Components of a Coal-Fired Boiler: Coal Feeder – Feeds coal to the boiler. Combustion Chamber (Furnace) – Burns the coal to generate heat. Heat Exchanger Tubes – Transfers heat to water to make steam. Steam Drum – Collects and separates steam from water. Flue Gas Stack – Expels exhaust gases after combustion. How Does It Work? Coal Combustion: Pulverized or crushed coal is fed into the combustion chamber where it burns at high temperatures. Water Heating: The intense heat turns water in the heat exchanger tubes into steam. Steam Power: The steam either drives turbines for electricity or possibly used for heating purposes in industries. Emissions Control: Modern systems can lead to scrubbers, electrostatic precipitators, and filters to cut back pollutants. Advantages of Coal-Fired Boilers High Power Output: They can handle large-scale industrial demands and provide a stable energy supply. Cost-Effective Fuel: Coal is generally more affordable and widely accessible than some alternative fuels. Established Technology: The infrastructure and maintenance knowledge are well-developed, driving them to reliable in many settings. Environmental Concerns While effective, coal-fired boilers will also be one of the largest options for environmental pollution. Key Issues: CO₂ Emissions: Major contributor to greenhouse gases and climate change. Particulate Matter: Causes respiratory issues and leads to air pollution. Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂) and Nitrogen Oxides (NOₓ): Lead to acid rain and smog. Ash Disposal: Handling of coal ash can cause health and environmental hazards. Innovations and Modern Solutions Efforts are being made to minimize the environmental impact of coal-fired boilers: Fluidized Bed Combustion (FBC) – Improves combustion efficiency and reduces emissions. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) – Captures CO₂ emissions for underground storage. Supercritical and Ultra-supercritical Boilers – Operate at higher pressure and temperature, enhancing efficiency. Emission Scrubbers and Filters – Remove pollutants from flue gases before they get to the atmosphere. Applications of Coal-Fired Boilers Power Plants – For electricity generation. Industrial Facilities – In cement, steel, and chemical manufacturing. District Heating – Provides centralized heat in colder regions. Paper and Textile Mills – Supplies process steam and heating. The Future of Coal-Fired Boilers As global environmental regulations tighten, the way forward for coal-fired boilers relies upon innovation and cleaner technologies. Many countries are gradually shifting toward alternative energy sources, nevertheless for some regions, particularly those with abundant coal reserves, transitioning might take longer. The key will probably be striking an account balance between energy needs, economic factors, and environmental responsibility. Coal-fired boilers have long served like a cornerstone of business progress. While their environmental drawbacks are significant, advancements in cleaner combustion technology and emissions control are helping to lessen their footprint. As energy landscapes evolve, coal-fired systems must continue adjusting to remain viable in the more sustainable future.
Main Components of a Coal-Fired Boiler: Coal Feeder – Feeds coal to the boiler. Combustion Chamber (Furnace) – Burns the coal to generate heat. Heat Exchanger Tubes – Transfers heat to water to make steam. Steam Drum – Collects and separates steam from water. Flue Gas Stack – Expels exhaust gases after combustion. How Does It Work? Coal Combustion: Pulverized or crushed coal is fed into the combustion chamber where it burns at high temperatures. Water Heating: The intense heat turns water in the heat exchanger tubes into steam. Steam Power: The steam either drives turbines for electricity or possibly used for heating purposes in industries. Emissions Control: Modern systems can lead to scrubbers, electrostatic precipitators, and filters to cut back pollutants. Advantages of Coal-Fired Boilers High Power Output: They can handle large-scale industrial demands and provide a stable energy supply. Cost-Effective Fuel: Coal is generally more affordable and widely accessible than some alternative fuels. Established Technology: The infrastructure and maintenance knowledge are well-developed, driving them to reliable in many settings. Environmental Concerns While effective, coal-fired boilers will also be one of the largest options for environmental pollution. Key Issues: CO₂ Emissions: Major contributor to greenhouse gases and climate change. Particulate Matter: Causes respiratory issues and leads to air pollution. Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂) and Nitrogen Oxides (NOₓ): Lead to acid rain and smog. Ash Disposal: Handling of coal ash can cause health and environmental hazards. Innovations and Modern Solutions Efforts are being made to minimize the environmental impact of coal-fired boilers: Fluidized Bed Combustion (FBC) – Improves combustion efficiency and reduces emissions. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) – Captures CO₂ emissions for underground storage. Supercritical and Ultra-supercritical Boilers – Operate at higher pressure and temperature, enhancing efficiency. Emission Scrubbers and Filters – Remove pollutants from flue gases before they get to the atmosphere. Applications of Coal-Fired Boilers Power Plants – For electricity generation. Industrial Facilities – In cement, steel, and chemical manufacturing. District Heating – Provides centralized heat in colder regions. Paper and Textile Mills – Supplies process steam and heating. The Future of Coal-Fired Boilers As global environmental regulations tighten, the way forward for coal-fired boilers relies upon innovation and cleaner technologies. Many countries are gradually shifting toward alternative energy sources, nevertheless for some regions, particularly those with abundant coal reserves, transitioning might take longer. The key will probably be striking an account balance between energy needs, economic factors, and environmental responsibility. Coal-fired boilers have long served like a cornerstone of business progress. While their environmental drawbacks are significant, advancements in cleaner combustion technology and emissions control are helping to lessen their footprint. As energy landscapes evolve, coal-fired systems must continue adjusting to remain viable in the more sustainable future.